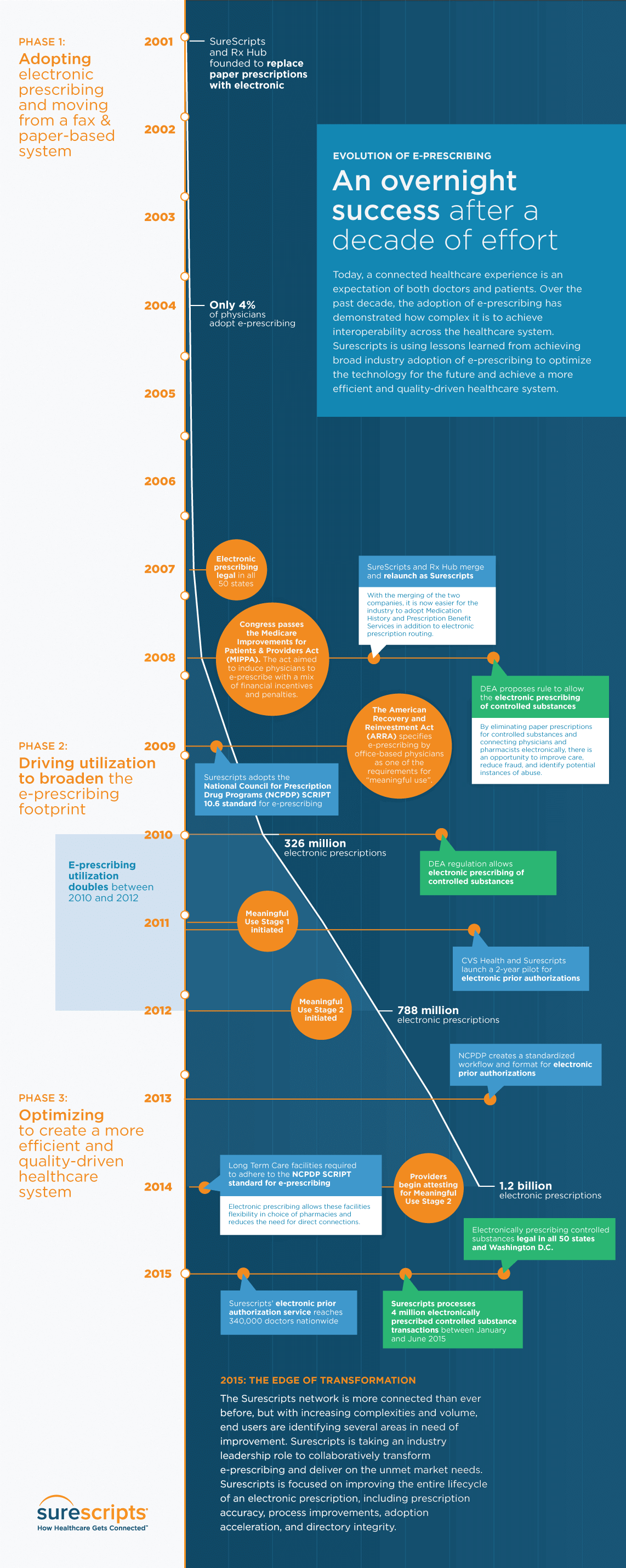
As National Health IT week kicks off its 10th anniversary, it’s worth reflecting on our achievements over the past 10 years and highlight one of the most successful examples of interoperability: electronic prescribing. Ten years ago, Surescripts built a nationwide network to connect doctors, hospitals, pharmacies, and health plans to enable the secure and efficient exchange of prescription information. Since then, that network has expanded to provide additional solutions including the e-prescribing of controlled substances, medication history, and electronic prior authorization, among others.
Our latest infographic shows how e-prescribing has evolved over time and is the first true example of interoperability. Here are a few highlights of this evolution:
- Electronic prescribing became legal nationwide in 2007 but it wasn’t until one year later, with the passing of the Medicare Improvements for Patients & Providers Act (MIPPA), that the industry reached the tipping point it needed to advance healthcare technology adoption and enable broad information exchange.
- Also in 2008, when then SureScripts merged with Rx Hub, it became easier for the industry to adopt critical information exchange capabilities through a single channel, including Medication History and Prescription Benefit Services, as well as electronic prescription routing.
- That same year, the DEA proposed a rule to allow the electronic prescribing of controlled substances (EPCS), a critically important milestone to improve care and reduce fraud related to highly addictive drugs.
- And with the advent of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act and creation of the Meaningful Use Program in 2009, the industry now had the incentives and penalties in place to fuel our collective progress even further.
- In 2010, the Surescripts network achieved a significant milestone, processing 326 million electronic prescriptions, then doubled utilization among prescribers and pharmacists between 2010 and 2012, with the introduction of Meaningful Use Stage 2 acting as an additional catalyst.
- And in 2014, the industry was given an opportunity to further extend electronic prescribing into new markets -- ones which stand to be greatly improved from its adoption -- with Long Term Care facilities being required to follow the NCPDP SCRIPT standard to which Surescripts had been adhering since 2009.
Fast forward to 2015: Surescripts’ electronic prior authorization service reaches 340,000 doctors nationwide, and we are on track to process 8 million electronic prescriptions of controlled substances this year. None of these achievements would have been possible without the necessary foundation of the early days of e-prescribing. While the ONC has given a 10-year window for the achievement of industry interoperability, we don’t have to wait that long -- or at all -- to see it in action. The lessons that can -- and must -- be learned from the evolution and continued adoption of e-prescribing are a clear roadmap for true interoperability.
Take a look below at our infographic for more information on the evolution of e-prescribing, and be sure to check back soon, for an even more in-depth look at how we’re optimizing e-prescribing to drive more value and improve quality going forward.


 Dean Riggott Photography
Surescripts
Dean Riggott Photography
Surescripts